| Sunrise |
Compute the fraction of the solar-disc area that is visible at specified times after the onset of sunrise.
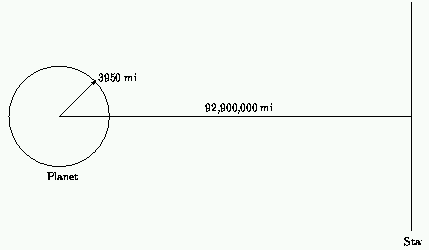
This is a two-body problem; there is a single planet and a single star.
Assume a perfectly spherical planet with a radius of 3950 miles. Ignore any possible atmospheric effects on the results to be determined.
At a distance of 92,900,000 miles from the planet's center is an illuminating class four star. For the determinations to be made in this problem, ignore anyphenomena arising from the orbital motion of the planet about the star and consider the illuminating star to be a planar disc. The plane in which the disc lies is perpendicular to the line between the planet center and the solar disc center. The solar disc has a radius of 432,000 miles.

Assume the planet rotates uniformly, making one full rotation in precisely 24 hours.
The sun is centered directly over the planet's equator during the entire revolution of the planet.
Let time be measured from when the first solar rays of the morning reach a given reference point on the equator. For each time value giveninthe input data stream, compute the fraction of the solar disc area that is illuminating this reference point on the equator.
The input time data are given as floating point values measured in seconds. There will be no time-data values less than zero, and none greater than 600. Each line of input will have one floating-point value that should be read using the default float/real input format.
Process the input data stream until the end-of-file is encountered.
Aline with a single real value is to be emitted for each input data value received. This value is to be the fraction of the solar disc (area) that is illuminating the reference point at the given time.
Answers must be rounded to six digits after the decimal point.
0.0 600.0
0.000000 1.000000